Abstract
Introduction: Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation is a cornerstone of therapy for hematologic malignancies and often a patient's only curative intent treatment. Overall outcomes for haploidentical transplantation appear to be excellent, however, this novel approach brings toxicities that are particular to its biological and clinical milieu. We previously described occurrence of severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS) after haplo-HCT. Severe CRS was associated with poor clinical outcomes, including transplant related mortality (TRM), overall survival (OS), and neutrophil engraftment (Abboud et al, BBMT, 10/2016). Furthermore, tocilizumab rapidly reversed the signs and symptoms of the dysregulated inflammatory reaction in most cases of CRS.
Here we compare short and long term complications in peripheral blood haplo-HCT patients who did and did not receive tocilizumab.
Patients and Methods: We performed a retrospective review of patients who underwent haplo-HCT transplantation at our institution from July 2009 through January 2017. A total of 169 patients were identified, 9% (15) received tocilizumab for treatment of CRS. We compared rates of acute and chronic GVHD, time to relapse, and incidence infection related deaths between patients who received tocilizumab and those who did not.
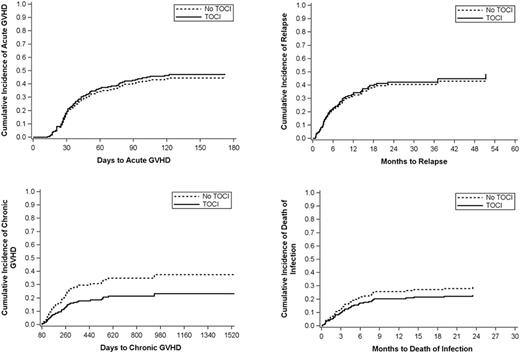
Results: We found no difference in acute GVHD (hazard 1.08, p 0.83), time to relapse (hazard 1.06, p 0.90), or incidence of infection related deaths (hazard 0.764, p 0.65) between patients who received tocilizumab and those who did not.
There was a trend towards a lower rate of chronic GVHD in patients who received tocilizumab compared with those who did not, with a hazard of 0.56 (95% CI 0.158 - 0.99, p= 0.37).
Conclusions: Tocilizumab is safe following haplo-SCT. Tocilizumab did not increase the risk of acute GVHD, chronic GVHD, time to relapse, or incidence of infection related deaths. There was a trend towards a lower rate of chronic GVHD in patients who received tocilizumab.
Uy: Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Travel Suppport; GlycoMimetics: Consultancy. Vij: Celgene: Honoraria; Konypharma: Honoraria; Bristol-Meyers-Squibb: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal